Hysterectomy & Oophorectomy
Hysterectomy & Oophorectomy
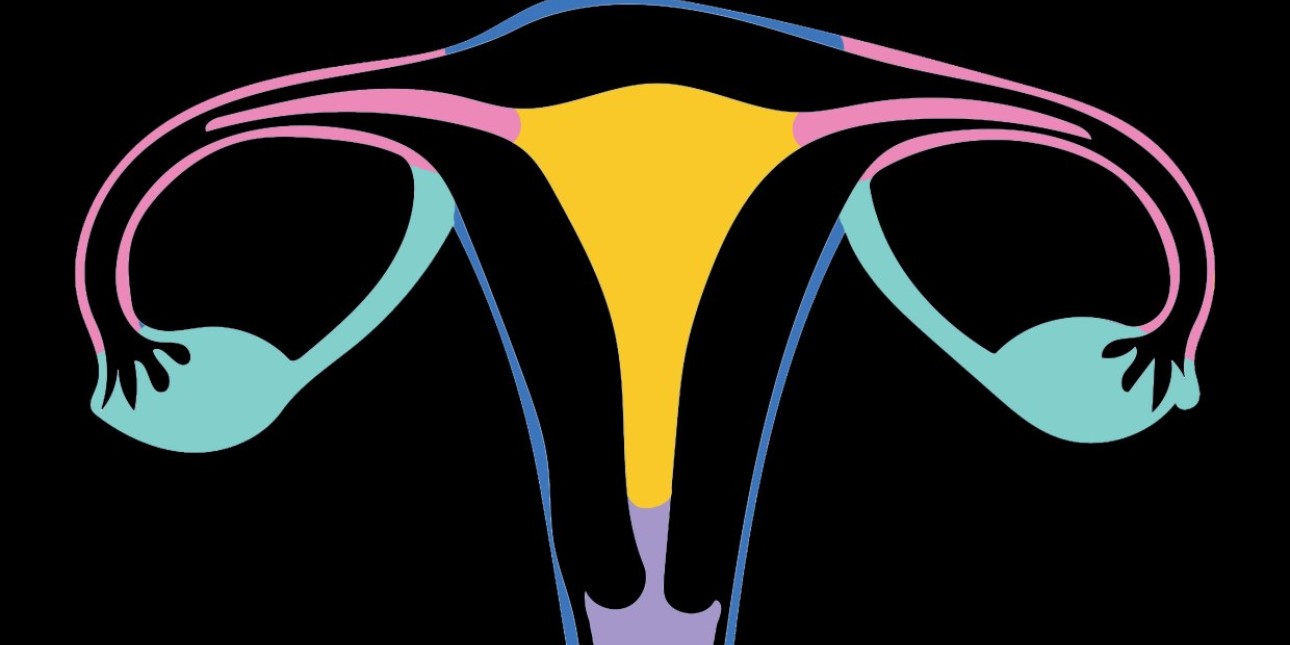
Hysterectomy is commonly used to refer to removing all internal reproductive organs: the cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries, although technically “hysterectomy” only means removal of the uterus.
Removal of the vagina (vaginectomy) is not a required part of hysterectomy or other genital surgeries (metoidioplasty and phalloplasty), but if you are planning to get a vaginectomy, hysterectomy will be performed in advance or at the same time.
If the cervix is removed, you no longer need to get monitoring pap smears.
Some people choose to leave one or both ovaries in the hope that they can function as internal estrogen hormone production when someone chooses to stop taking testosterone or loses access to testosterone.
Long term, you need to have either testosterone or estrogen in order to maintain bone density and for energy and mood.
Some people choose to leave ovaries in order to retain material to genetically reproduce with later.